What is Cervical Radiculopathy
Experiencing intense neck pain with tingling?
Often people with cervical radiculopathy (CR) in Singapore mistake for musculoskeletal disorders and stress-related neck pain because it’s more common. Only when the symptoms other than pain including sensory disturbances such as burning sensation, pin and needle prick, loss of muscle function and weakness become apparent they seek treatment. If the pain in your neck is radiating or is spread across your shoulder and arms, it could be CR.
What is cervical radiculopathy?
Cervical Radiculopathy refers to dysfunction, irritation or damage to a nerve or group of nerves that exit the spinal cord and branch into the neck, arms, or shoulders. A disc from any of the seven cervical vertebrae when pinches or presses against the nerves that connect to the spinal cord may result into CR. Commonly this condition is called a pinched nerve. The symptoms radiate along the length of nerves that travel across neck, chest, arm, and shoulders.
What are the symptoms of cervical radiculopathy?
The symptoms of cervical radiculopathy include
- Muscle weakness
- Neck muscle spasm
- Tingling and numbness in the hands and fingers,
- Shooting pain in the shoulders, neck, chest and upper back.
- Lack of hand coordination
How long does it take to heal from cervical radiculopathy?
Depending on the severity, the time to recover or heal varies. Generally, a person with acute radiculopathy following nonsurgical treatment will feel better in 6 to 12 weeks. But this can extend to six to twelve months in some instances. Those who have lost sensation, muscle power and experience severe pain might need a surgery to get relief. In such cases, a general physician will refer a patient to a neurosurgeon for specialized treatment.
What causes cervical radiculopathy
Pressure on the nerve roots due to
- Degenerative bone changes,
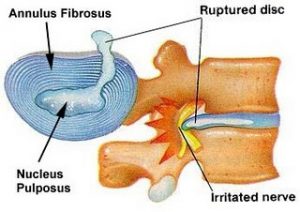
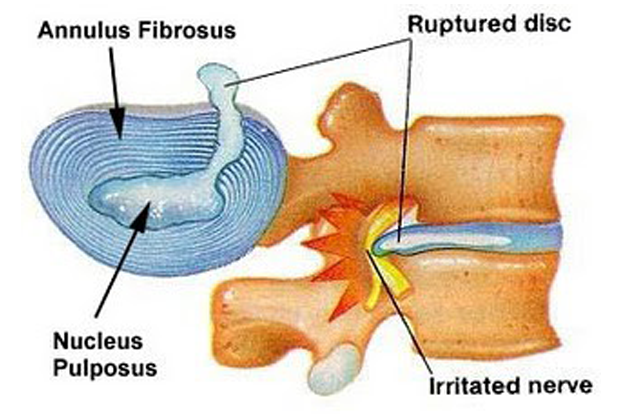
- Ruptured disc,
- Disc herniation,
- Neck arthritis,
- Acute injury,
- and other neck and back related injuries cause cervical radiculopathy.
People who are middle-aged can suffer cervical radiculopathy due to degenerative disc changes. Younger people who went through back trauma are likely to get develop cervical radiculopathy. Ruptured disc causing inflammation and compression of disc material usually trigger this condition. Based on the studies by Tan Tock Seng Hospital in Singapore around 20 to 30% of people with disc herniation had to deal with acute pinched nerve.
People Also Read: What Is Cervical Spondylosis? A Complete Guide to Neck Arthritis
How to know if you have Cervical Radiculopathy
While the symptoms of cervical radiculopathy could be related to other conditions such as carpal tunnel, sclerosis, and angina, distinguishing between them and getting an accurate diagnosis from a doctor is important. A doctor will check your medical history and perform a physical exam to determine the problem. In case you had to go through an accident or injury in the past, the doctor will investigate if it is causing the current symptoms. Lifestyle and family history are also considered. While performing the physical exam doctor will palpate the neck to check tenderness, abnormalities, the range of motion and neck strength. To get conclusive evidence, a doctor will do a Spurling test, which is a part of the physical exam where gentle pressure is applied on the top of the head to compress the cervical spine. If the symptoms temporarily or of the moment worsen, it largely confirms the presence of cervical radiculopathy.
For more information, please contact www.rapidphysiocare.com or call +65 6904 4900
Tags : Physiotherapy