Carpal Tunnel Syndrome(CTS)
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
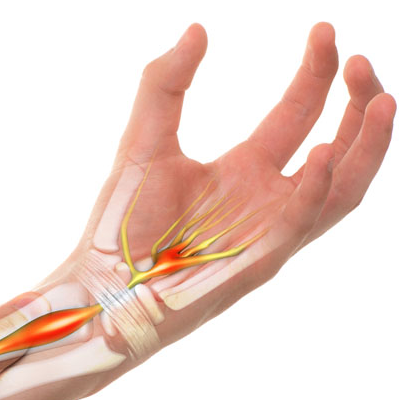
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common nerve entrapment syndrome, where the median nerve gets compressed in the carpal tunnel. The median nerve runs along the forearm passing through the wrist ending at the tip of the fingers. This nerve controls the movement and sensations of the first four fingers. The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway formed by the ligaments and the carpal bones located at the wrist.
Causes of CTS
For most cases, the cause of this condition is a combination of several risk factors. This includes repetitive movements of the wrist, working in a cold environment and forceful hand work. Workers who are more susceptible for CTS may include clerical clerk who does computing work, workers in the construction and factories which requires heavy lifting, mechanics and dentist.
Besides that, swelling and inflammation of the carpal tunnel from conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or a wrist fracture may cause narrowing of the space in the carpal tunnel leading to irritation of the nerve. Other conditions such as diabetes, gout, hyperthyroidism, obesity and pregnancy also increase the prevalence of getting it.
Symptoms of CTS
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers.
Numbness and sensations like electrical shocks is usually felt in the thumb and the first three fingers of the hand. The sensation may travel up from the wrist to the forearm. Activities such as driving, holding a phone or reading a book may easily trigger the symptoms. Often, a person with CTS will have the urge to ‘shake’ the hand to relief the symptom.
- Weakness in the hand and wrist
Weakness in the hand and arm strength may develop, the strength between both hands may vary. In some severe cases, there may be obvious muscle wasting (thenar) at the base of the thumb.
- Inability to perform task which requires delicate motions
Buttoning a shirt or picking up a coin from a smooth surface may seem difficult
- Dropping object
Eventually, frequent dropping of object, especially small objects may happen due to the lack of sensation and strength

Diagnosis
- Medical history
Examination usually starts with asking questions to collect information about the medical history and the onset of symptoms.
- Physical examination
Physical examination of the hands, arm, shoulder and neck. Checking for any tender, swelling discoloration, sensation and strength to eliminate other causes of pain at the hand and wrist.
Specific test which are used to reproduce the symptoms:
Tinel’s Sign
In this test is, tap or press over the median nerve located on the wrist for few times. It is considered positive when there is a tingling sensation in the fingers.
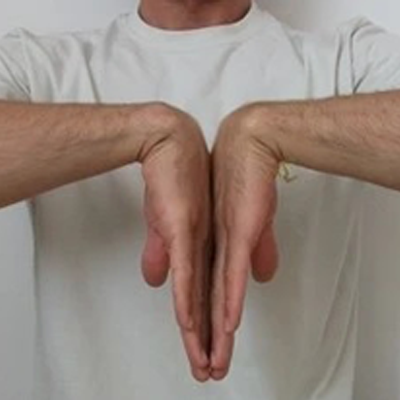

Phalen’s test
This is a provocative test done to compress or squeeze the median nerve at the wrist. In this test, press the back of the palm together and hold it for 1 minute. The test is positive when there is numb or tingling sensation in the fingers.

