Ankle Sprain Physiotherapy Treatment
An ankle sprain is a common injury that happens when the ankle twists, rolls, or turns over its normal movement range. This sudden movement can overstretch or tear the ligaments that support the ankle joint. Without timely treatment, even a mild injury can affect balance, walking, and long-term joint stability.
At Rapid Physiocare, we provide proven ankle sprain physiotherapy focused on pain relief, healing, and full functional recovery. Whether you have a sprained ankle, ankle ligament injury, or lingering pain after a twisted ankle, early physiotherapy helps you recover faster and safer.
The Major Ankle Ligaments
The ankle joint is supported by a complex network of bones and ligaments that work together to provide strength, balance, and controlled movement. These ligaments act as strong fibrous bands that stabilize the joint and protect it during daily activities and sports. When excessive force is applied, these structures can stretch or tear, leading to an ankle sprain and instability if not treated properly.
The ligaments of the ankle are grouped into three main categories, with the lateral ligaments being the most.
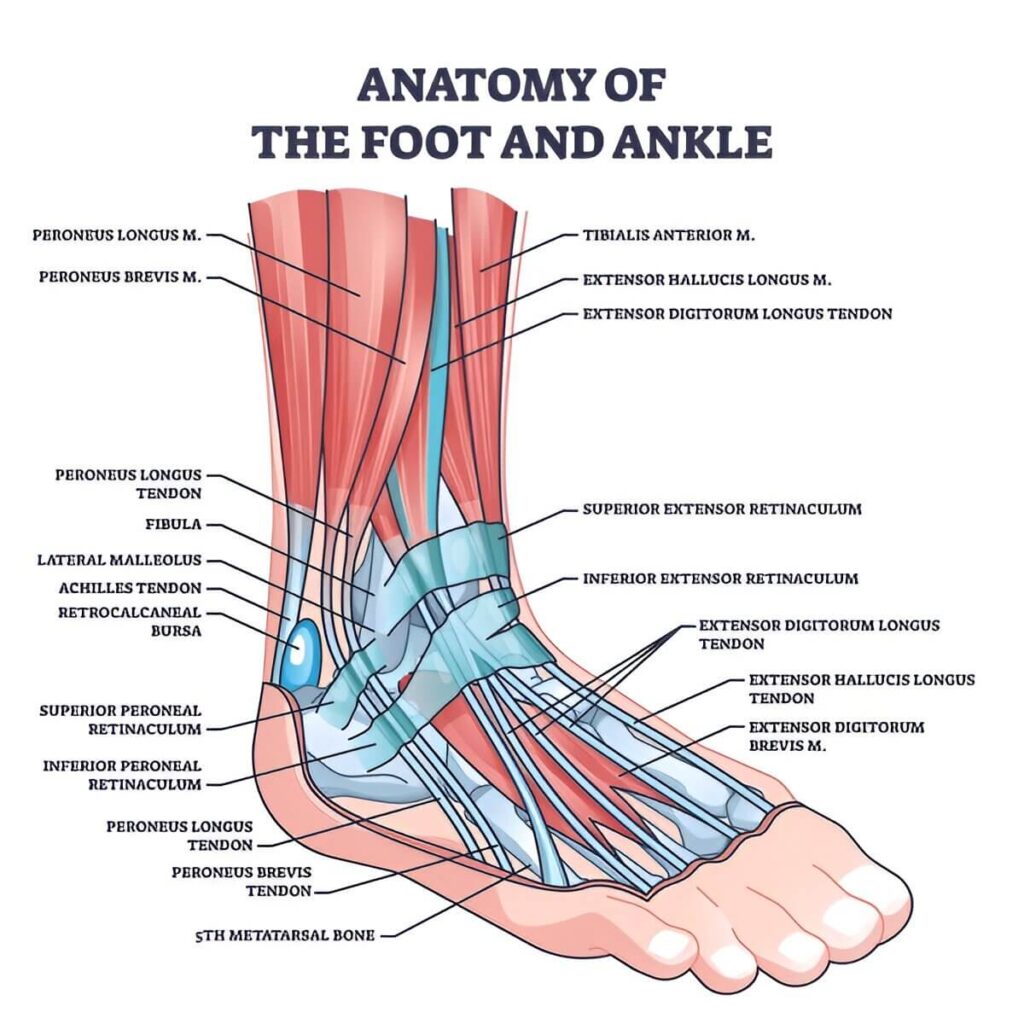
The three key ligaments include:
- Anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL): Connects the front of the talus bone to the fibula and is the most injured ligament in an ankle sprain
- Calcaneofibular ligament (CFL): Connects the heel bone (calcaneus) to the fibula and supports side-to-side stability
- Posterior talofibular ligament (PTFL): Connects the back of the talus bone to the fibula and provides support during severe injuries
In most cases, damage to the ATFL leads to pain, swelling, and instability requiring ankle sprain physiotherapy.
Ankle Sprain Symptoms
Understanding the symptoms helps you seek care before the injury worsens.
Common signs include:
- Swollen ankle
- Pain during walking or standing
- Bruising and tenderness
- Reduced ankle movement
- Feeling of instability or weakness
Ankle fractures are common injuries most often caused by the ankle rolling inward or outward. Many people mistake an ankle fracture for an ankle sprain, but they are different and, therefore, will require an accurate and early diagnosis.
Persistent symptoms may indicate a deeper ankle ligament injury, fractured ankle, or broken ankle, which requires professional assessment.
Ankle Sprain Causes
Ankle sprain causes are usually linked to sudden stress on the ankle ligaments when the joint is forced beyond it’s normal movement range. When the foot rolls inward or outward unexpectedly, it can overstretch or tear the supporting ligaments. Poor muscle control, weak balance, or previous injuries reduce the ankle’s ability to stabilize itself during movement. Without proper recovery and physiotherapy, the ligaments remain weak, increasing the risk of repeat sprains and long-term ankle instability.
Common causes include:
- Sudden twisted ankle while walking or running
- Sports involving jumping or quick direction changes
- Uneven surfaces or poor footwear
- Weak ankle muscles or poor balance
- Previous ankle sprain without proper rehab
Type of Ankle Sprain Injury
Different ankle sprains affect the ligaments in different ways. The severity of ligament damage determines pain level, swelling, stability, and recovery time. Understanding the grade of injury helps in choosing the right treatment and preventing long-term ankle problems.
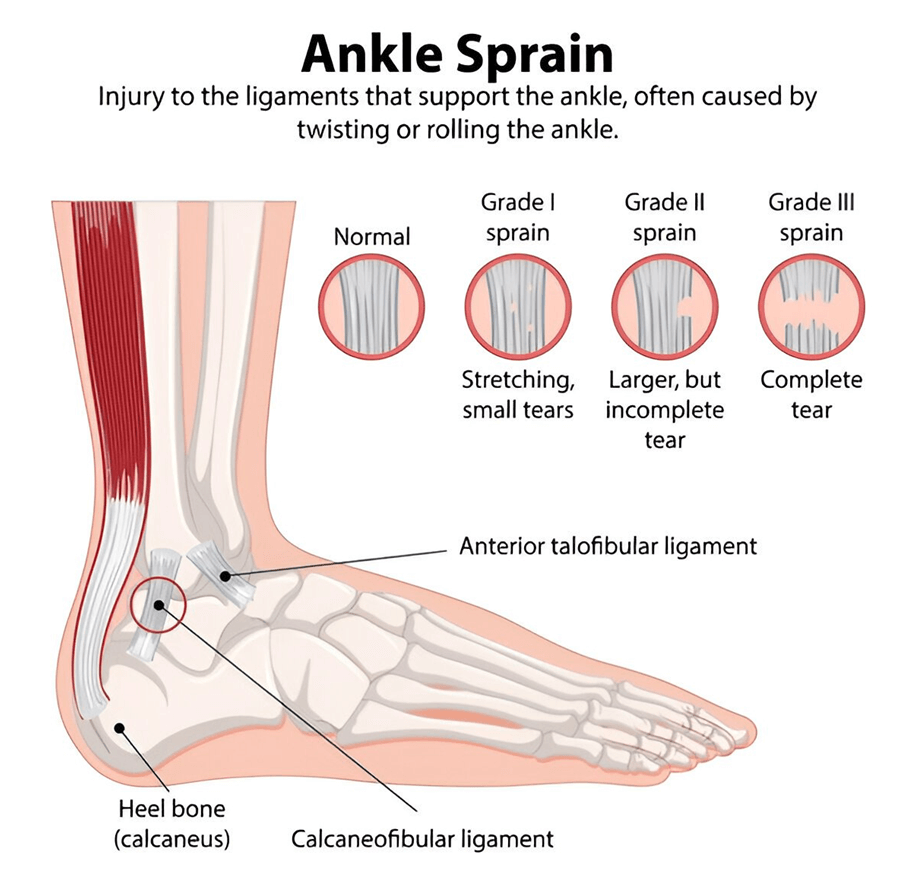
Grade 1 ankle sprain: Mild Ankle Sprain
A Grade 1 ankle sprain occurs when the ligaments are overstretched but not torn. The ankle remains stable, and pain is usually mild. Swelling and tenderness are minimal, and walking is still possible with slight discomfort. Early care and basic physiotherapy help restore movement quickly and prevent recurrence.
Grade 2 ankle sprain: Moderate Ankle Sprain
A Grade 2 ankle sprain involves a partial tear of one or more ankle ligaments. This causes noticeable swelling, bruising, and pain, making walking uncomfortable. The ankle may feel weak or unstable during movement. Physiotherapy is essential to support healing, improve strength, and restore joint stability.
Grade 3 ankle sprain: Severe Ankle Sprain
A Grade 3 ankle sprain is the most serious form, involving a complete ligament tear. Severe pain, significant swelling, and bruising are common, and weight-bearing is often impossible. The ankle becomes unstable and requires structured rehabilitation. Timely physiotherapy is crucial to regain strength, mobility, and prevent chronic ankle instability.
Care and Treatment for Ankle Sprain
Effective ankle sprain treatment focuses on healing the injured ligament while restoring ankle strength, stability, and normal movement. Early care reduces swelling, prevents stiffness, and lowers the risk of long-term instability. Treatment is always based on the grade of ankle sprain, as each level requires a different rehabilitation approach.
Treatment includes:
- Pain and swelling management
- Controlled mobility and joint support
- Manual therapy for joint alignment
- Progressive ankle sprain exercises
- Support for ankle ligament tear treatment
Proper care improves ankle ligament tear recovery and prevents future injuries.
What Should I Do When I Sprain My Ankle?
- Rest: Stay off the injured ankle. Walking may cause further injury.
- Ice: Apply an ice pack to the injured area, placing a thin towel between the ice and the skin. And do a couple of times for 20 minutes with a 40-minute interval.
- Compression: An elastic wrap may be recommended to control swelling.
- Elevation: The ankle should be raised slightly above the level of your heart to reduce swelling.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation. In some cases, prescription pain medications are needed to provide adequate relief.
- Early physical therapy.
How Rapid Physiocare Helps You
Unfortunately, a sprained ankle can increase your risk of re-injury by as much as 40-70%. But with the correct post-injury rehabilitation exercises, this risk can be significantly reduced.
Several sprained ankle physiotherapy treatments need to be employed to effectively rehabilitate your sprained ankle and prevent recurrence.At Rapid Physiocare, we focus on complete recovery, not just short-term relief.
Key Benefits:
- Personalized ankle sprain treatment plans
- Expert physiotherapists for ligament injuries
- Advanced ankle injury physiotherapy techniques
- Faster healing and improved mobility
- Reduced risk of recurrent ankle sprain
- Support for post-fractured ankle or broken ankle rehab
Our Ankle Sprain Therapy Process
Step 1: Detailed Assessment
We assess pain, swelling, joint stability, and movement patterns.
Step 3: Targeted Rehabilitation
Customized ankle sprain exercises restore strength and flexibility.
Step 5: Return-to-Activity Guidance
Safe return to sports, work, and daily movement.
Step 2: Pain & Swelling Control
Early therapy reduces inflammation and protects the ligament.
Step 4: Balance & Stability Training
We prevent future ankle sprains by improving coordination.
Book Your Recovery Session Now
At Rapid Physiocare, we help patients move freely, enjoy life without pain, and get back to doing all the things they love. Let’s start your recovery journey with Rapid Physiocare and get your sprain-free ankle
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does ankle sprain recovery take?
Recovery depends on severity. Mild sprains heal in 1–2 weeks, while severe injuries may take 6–12 weeks with physiotherapy.
Starting physiotherapy early helps reduce stiffness and speeds up recovery. Avoid rushing back to sports too soon as it can cause re-injury.
Can I walk with a swollen, sprained ankle?
Walking too early may worsen the injury. Professional assessment is advised. If your ankle hurts when you walk or feel unstable, don’t force it.
Use crutches or a brace for support in the early days. Once pain and swelling reduce, your physiotherapist will guide you on safe walking and weight-bearing exercises to rebuild strength and balance.
What is the best ankle ligament tear treatment?
Early physiotherapy improves ankle ligament tear recovery and reduces chronic pain risk.
Follow the R.I.C.E. method right after injury:
- Rest– Stop activities that cause pain.
- Ice – Apply an ice pack for 15–20 minutes every few hours.
- Compression– Use a bandage to reduce swelling.
What is the best exercise for a sprained ankle?
Start with gentle range-of-motion and balance exercises once pain reduces.
Examples:
- Ankle circles to loosen the joint.
- Towel stretch to improve flexibility.
- Heel raises to rebuild calf strength.
- Single-leg balance to retrain stability.
Always progress gradually under a physiotherapist’s supervision. Doing exercises too early or too aggressively can slow recovery.
Is physiotherapy necessary for a sprained ankle?
Yes. Physiotherapy for ankle sprains ensures proper healing and prevents long-term instability.
Can ankle sprains become chronic?
Yes. Without rehab, they may develop into a chronic ankle sprain or recurrent ankle sprain.

